The longest
hair on your body, hair!
There's
nothing you can do to prevent your hair from getting damaged,
whether it's from
styling, coloring, perming, UV rays, fine dust, or anything else.
Hair damage
always starts at the end of the hair, which is the "cuticle" as we
know it.

You've
probably heard that open cuticles cause a lot of hair damage.
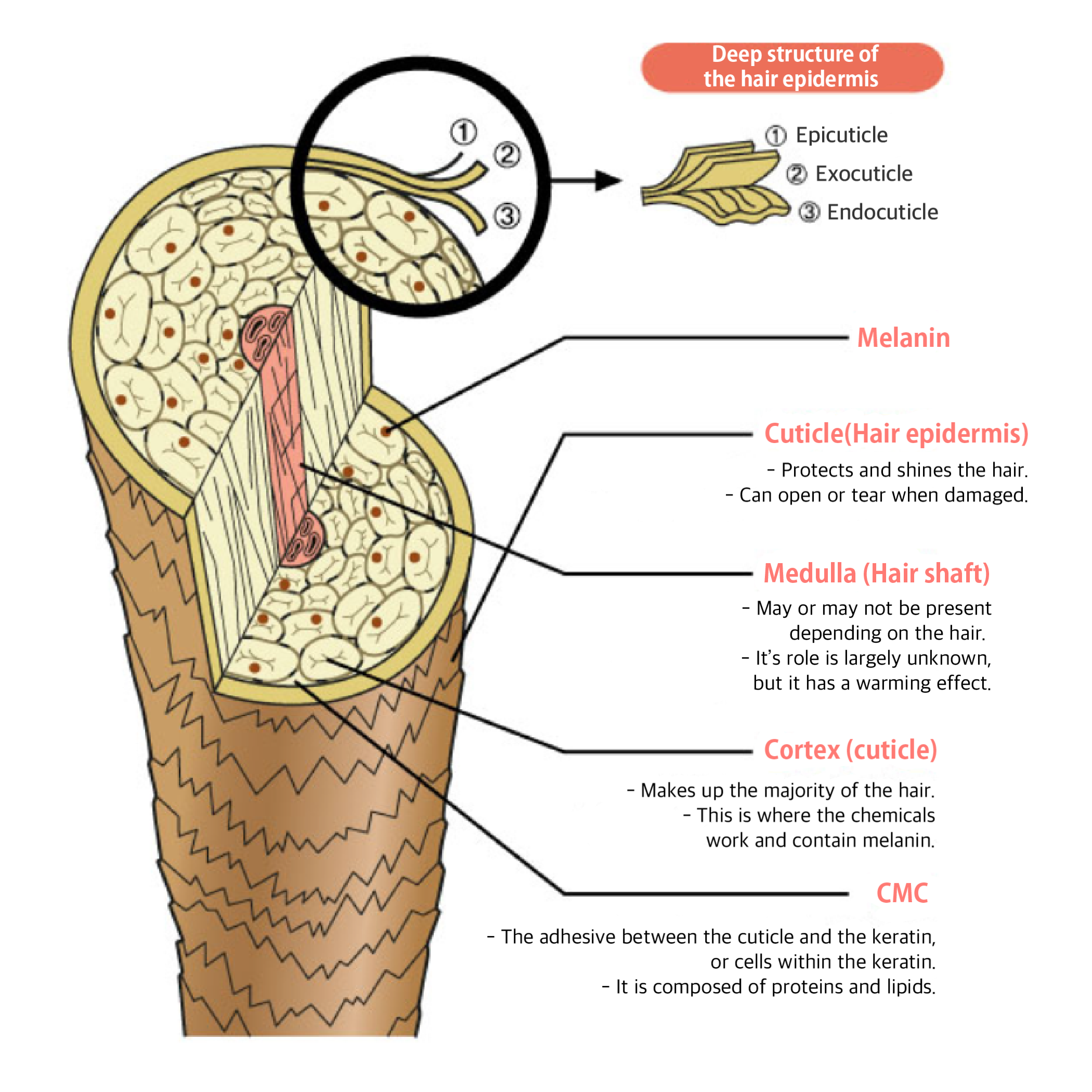
Damaged
hair starts with a damaged cuticle.
Why is
damaged hair dull and rough? Because the cuticle is lifting, and the light is
reflected off, making it hard to see the shine. And the cuticles are tangled
together, making the hair feel rough. Also, CMC, the glue of the cuticle, is
lost for various reasons, resulting in a lack of shine, softness, and moisture.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What is the cuticle, the first place you can see how
damaged your hair is?
What is the
cuticle?
The cuticle
is the outermost layer of the hair shaft.
"a
lamellar structure that covers the cell surface of the outermost layer of an
organism.
Hair is
made up of more than 95% protein, and it has the same structure as a Gimbap.
The cuticle
(hair epidermis) is the equivalent of the seaweed in Gimbap, the cortex (hair
cortex) is the equivalent of rice, and the medulla (hair medulla) is the
equivalent of ham.
More than
75% of the total area of the hair is made up of cortex cells, 15% is made up of
the epidermis, 3.5% is made up of the CMC, and about 3% is made up of the
medulla.
The
outermost part of the hair is the cuticle, and the more layers of cuticle
tissue you have, the stronger, shinier, and healthier your hair will be. The
cuticle has a respiratory function, and if it is missing from the hair, it
cannot fulfill its physiological function.
* What is
CMC?
- CMC
stands for Cell Membrane Complex.
- The
membrane that connects cuticle to cuticle,
* Role of
the CMC
- The glue that holds cuticle to cuticle.
- The glue that holds the cells in the keratin
together
- Keeps moisture and protein in the hair protected
from external stimuli
- Penetration channel for nutrients
* CMC
Composition
- Lipids
- Proteins
There are
three main types of cuticles, based on where they are located and the cuticle
is made up of a complex of cell membranes.
*
Epicuticle
- The
outermost part of the hair epidermis.
- It
receives primary stimulation from chemical treatments and external aggression,
and is weak against physical stimuli but very resistant to chemical attack.
*
Exocuticle
- A very unstable layer that lies inside the
epicuticle and is intermediate to alkaline chemicals.
- Easily attacked by chemicals such as perms
and hair dyes.
*
Endocuticle
- Innermost layer of the hair cuticle,
bordering the cortex.
- It is hydrophilic and weakly resistant to
alkaline products, and the presence of cell membrane complexes (CMCs) serves to
adhere to the adjacent epidermis.
Healthy hair
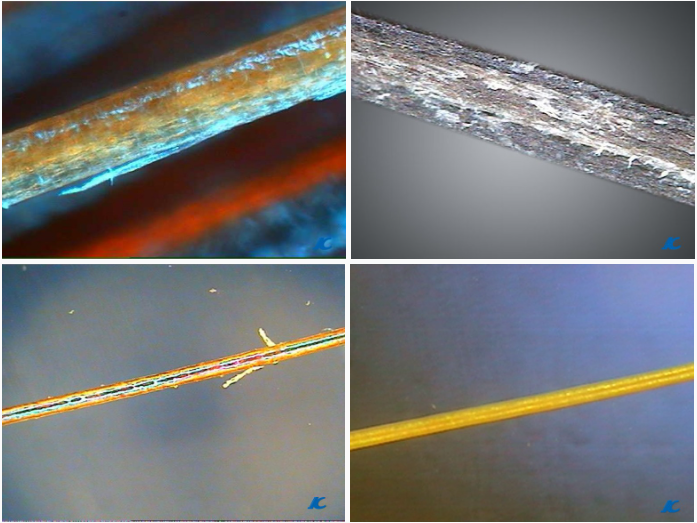
Damaged
Hair
The
outermost layer, the epicuticle, has about 12% cystine, the exocuticle has
about 50%, and the endocuticle has about 3%. The more cystine, the more
hydrophobic (water-averse) and rigid the structure.
When hair
is immersed in water, the endocuticle, the innermost part of the cuticle,
swells by its own volume, causing the entire cuticle to open.
Because the
cuticle is layered with CMC and is microscopic, large molecules cannot
penetrate it, but if it is swollen and softened by an acid or alkali to create
a gap, larger molecules can enter.
The cuticle
also breathes to different degrees depending on humidity. Since the superficial
CMC runs through the entire hair, water is absorbed into it and the endocuticle
swells, opening up the entire cuticle.
<These are clinical photos taken with a
specialized electron microscope>
*Reference:
- Optical
microscope: A device that utilizes the refraction of light to magnify and
observe tissue or conditions, such as our product.
- Electron
microscope: A device that uses an electric or magnetic field to focus an
electromagnetic current onto an electronic lens, magnifying the image of a
sample placed in its path. It has much greater resolving power than an optical
microscope.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How can we prevent this cuticle damage?
Many people
know that it gets damaged, but they don't know why it gets damaged.
Did you
know that the cuticle is not on the end of the hair?
The cuticle
is nowhere to be found towards the bottom, as the hair loses its ability to
retain moisture inside, which causes it to dry out, and the friction of combing
and other forms of breakage further damages the hair.
That's why
it's so important to take care of the hair shaft, the part of the hair we know
as the dead protein.

The lower
part of a healthy hair
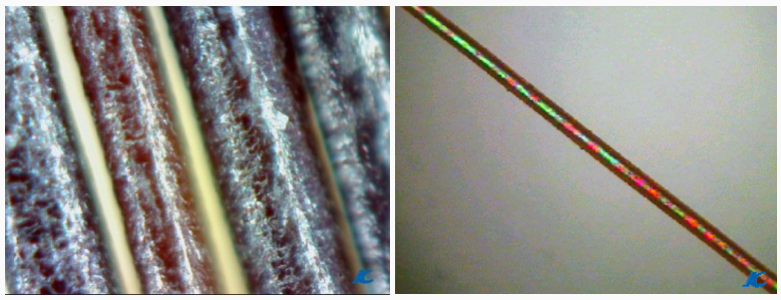
Bottom of
damaged hair
Nowadays,
everyone wants to have healthy hair.
However,
hair that has been damaged even once due to frequent dyeing or perming, fine
dust, UV rays, etc. cannot be repaired naturally.
Therefore,
it takes effort and time to repair your hair.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
So, what are some at-home hair care tips you can do?
-
'Brushing' with a comb before washing your hair
- Rinse
with plenty of water after shampooing
- Apply
treatments to hair and leave for a few minutes to absorb
- Apply
essence or pack care products after drying your hair
-
Blow-drying your hair with cool air rather than hot air
These tips
will help you do less damage to your hair.
Keep your
scalp and hair healthy with accurate scalp and hair diagnosis and care :)
* Sources:
Scalp and Hair Care Utilizing NCS (Gunja Publishing), Scalp and Hair Care (Bukk
Publishing), Scalp and Hair Care (Guminsa), Scalp and Hair Care (Chunggu
Culture),Scalp and Hair Care (Medisian Publishing)
* Image
source: Canva